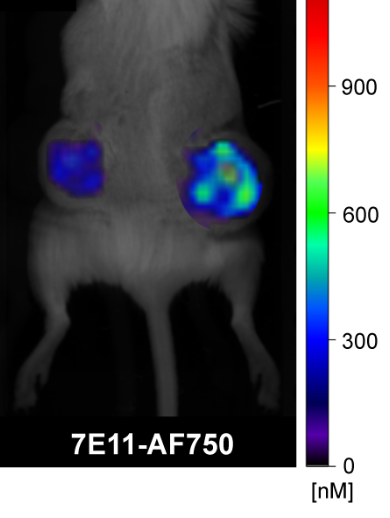
PSMA is a dimeric type II integral membrane glycoprotein, highly expressed on prostate cancer cells. It has been shown to be a predictor for prostate cancer progression and for prognosis of prostate cancer. For example, elevated PSMA levels are seen in aggressive forms of the disease, i.e., metastatic and higher-grade prostate cancers. High-level PSMA expression is correlated with early PSA recurrence in surgically treated prostate cancer. PSMA correlates with the aggressiveness of the disease, and thereby strongly support PSMA as an excellent target for prostate cancer characterization and subsequent therapy.
Our lab is interested in using nanoparticles as nanocarriers for drugs to improve prostate cancer therapy and small molecular agents to quantify PSMA expression in vivo. Many of our agents, described in the other projects (nanoagents and activatable imaging agents), are geared toward PSMA. Beyond that, we have a particular interest in the biological and enzymatic function of PSMA as it pertains to tumor promotion and vascularization.
We are further exploring ways to better characterize sentinel lymph nodes in prostate as well as in other cancers (e.g., endometrial and breast). We recently developed positron lymphography, a concept that is being expanded currently in the lab.

