This information explains the causes and symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and how to treat it.
About GERD
GERD is a disorder where the contents of your stomach flow back into your esophagus. Your esophagus is the tube that carries food and liquids from your mouth to your stomach (see Figure 1).
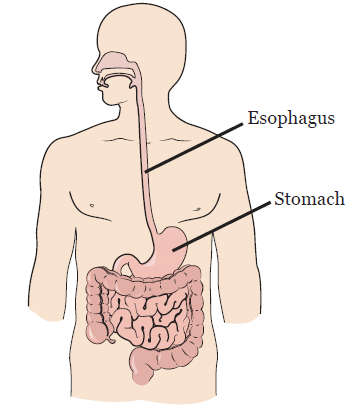
GERD can cause esophagitis (ee-SAH-fuh-JY-tis). This when the lining in your esophagus is inflamed (red and swollen). If you do not treat esophagitis, it can cause ulcers (sores), bleeding, and narrowing in your esophagus. It may also increase your risk for esophageal cancer.
Causes of GERD
GERD can be caused by many things, including:
- Eating large meals.
-
Eating and drinking large amounts of:
- Fried or fatty foods.
- Spicy foods.
- Citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, and limes.
- Chocolate.
- Mint.
- Tomatoes.
- Caffeinated drinks, such as coffee, tea, and soda.
- Exercising after a meal.
- Lying down, especially after meals. This can make it easier to regurgitate food. (when food moves from your stomach into your esophagus). This can create a sour, acidic taste in your mouth, caused by your stomach fluid.
- Smoking.
- Drinking alcohol.
- Having a hiatal hernia (when the top of your stomach bulges through your diaphragm). Your diaphragm is the muscle that separates your abdomen (belly) and chest.
- Pregnancy.
- Obesity (having a high, unhealthy amount of body fat).
-
Pressure on your abdomen. This can happen if you:
- Strain while having a bowel movement (pooping) due to constipation (having fewer bowel movements than usual).
- Strain while coughing, bending, or lifting.
- Wear pants that are too tight in the waist. This pressure can squeeze stomach contents up and into your esophagus.
Symptoms of GERD
The symptoms of GERD may include:
- Heartburn that usually happens 30 to 60 minutes after eating.
- Regurgitation.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Chest pain.
- Cough.
- Sore throat.
- Feeling like you have a lump in your throat.
How to treat GERD
The goal of treatment for GERD is to reduce your symptoms. Most people feel better with medicine and lifestyle changes.
Here are some ways you can reduce your GERD symptoms:
- Do not eat large meals. Eat smaller meals more often. This will allow you to eat the same amount of food, but in portions that are easier to digest.
- Do not lie down for at least 2 to 3 hours after eating.
- Avoid late-night snacks.
-
Avoid some foods, such as:
- Peppermint and spearmint candy, gum, and mints.
- Fried or fatty foods.
-
Avoid some drinks, such as:
- Acidic juices, such as orange juice.
- Alcohol.
- Peppermint and spearmint tea.
- Caffeinated drinks, such as coffee and tea.
- Carbonated (fizzy) drinks, such as soda.
- Take antacids (medicine that relieves the acid in your stomach) or sit upright to reduce heartburn.
- Do not smoke cigarettes or use other tobacco products. MSK has specialists who can help you quit smoking. To learn more about our Tobacco Treatment Program, call 212-610-0507 or ask your MSK healthcare provider.
- Use blocks to raise the head of your bed or sleep on a wedge pillow to raise your upper torso. This can help with symptoms at night. You can buy a wedge pillow from your local pharmacy or health supply store.
-
Avoid putting pressure on your abdomen.
- Limit bending and vigorous exercise after eating.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing.
- Prevent or manage constipation. Read Managing Constipation to learn more.
- Maintain a healthy body weight through diet and physical activity. Read Eat Your Way to Better Health to learn more about making healthy food and exercise choices.
- Take any medicine your doctor prescribes you as instructed.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider if:
- Your symptoms do not get better after trying the treatments above.
- You have trouble swallowing.
