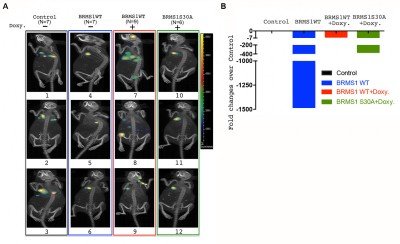
In LUAD, p53 mutations occur more commonly (45%) than KRAS, EGFR, or ELM4/ALK genomic alterations, combined. Previously, we have shown that BRMS1-mediated suppression of cell migration and invasion is associated with loss of p53. An unbiased analysis of the TCGA database reveals low BRMS1 expression is associated with more lymphovascular invasion and worse progression-free survival in p53mut LUAD and LUAD with solid histologic subtype. Our lab has identified that BRMS1 suppresses metastasis through multiprotein HDAC transcriptional co-repressor complex or as an E3 ligase to control p300 acetyltransferase levels. We have also shown that BRMS1 is repressed both at the transcriptional level by DNMT1 and post-translationally by CK2-induced phosphorylation and proteosome degradation (Figure 1). Using a CK2 inhibitor (CX4945), we have been able to rescue the expression of BRMS1 and repress metastases, showing BRMS1 may be therapeutically targetable. We have also found that the homozygous SNP rs1052566 in BRMS1v2 (BRMS1v2A273V/A273V) is present in 8% of patients with LUAD and correlates with tumor aggressiveness. We discovered that inactivation of nuclear Src mediates the accumulation of intratumoral c-fos in patients with BRMS1v2A273V/A273V LUAD, which promotes metastases. Using a patient-derived organoid (PDO) metastasis model, we utilized a c-fos inhibitor to suppress metastases in BRMS1v2A273V/A273V LUAD (Figure 2). To better characterize mechanisms of action and functional assessments in vivo, we have also generated the first Brms1-/- transgenic mouse by crossbreeding GEMM and a mouse cell line, obtaining transgenic mice with oncogenic KRAS+/LSL-G12D/ p53fl/fl with different Brms1 profiles (Brms1-/-, +/+, +/-) (KPB mice) (Figure 3). We continue to use our PDO model and novel BRMS1-/- transgenic mice to further understand the transcriptional mechanisms of BRMS1-mediated suppression of metastases in p53mut LUAD. We collaborate with the Marty W. Mayo Laboratory, the Jorge Reis-Filho Laboratory, and the Prasad S. Adusumilli Laboratory.